16S/ITS Amplicon Sequencing
16S rRNA gene is present in the genome of all bacteria and represents the DNA sequence corresponding to the bacterial-encoded rRNA. Its high degree of conservation and specificity serves as a molecular "ruler" for bacterial evolution. 16S rDNA sequencing refers to a technique that involves PCR amplification and high-throughput sequencing of the hypervariable regions of the 16S rRNA gene from environmental samples, widely used for rapid identification of microbial communities in samples.
In eukaryotic rDNA, the transcribed spacer sequences between 18S rDNA and 28S rDNA are referred to as ITS (Internal Transcribed Spacer). The region between 18S and 5.8S is known as ITS1, while the region between 5.8S and 28S is called ITS2. The gene sequences of 18S, 5.8S, and 28S are conserved and show minimal variation among most organisms. In contrast, the non-transcribed ITS1 and ITS2 regions experience lesser natural selection pressure during evolution, allowing for more variations. These regions exhibit extensive sequence polymorphism in the majority of eukaryotes and can be utilized for fungal classification and identification.
 Platform and Strategy
Platform and Strategy
Platform and Strategy
Illumina sequencing platform,PE250
Genomic DNA extraction
Design and synthesis of primers
PCR amplification and purification of products
Quantification and normalization of PCR products
Illumina sequencing
Bioinformatics analysis
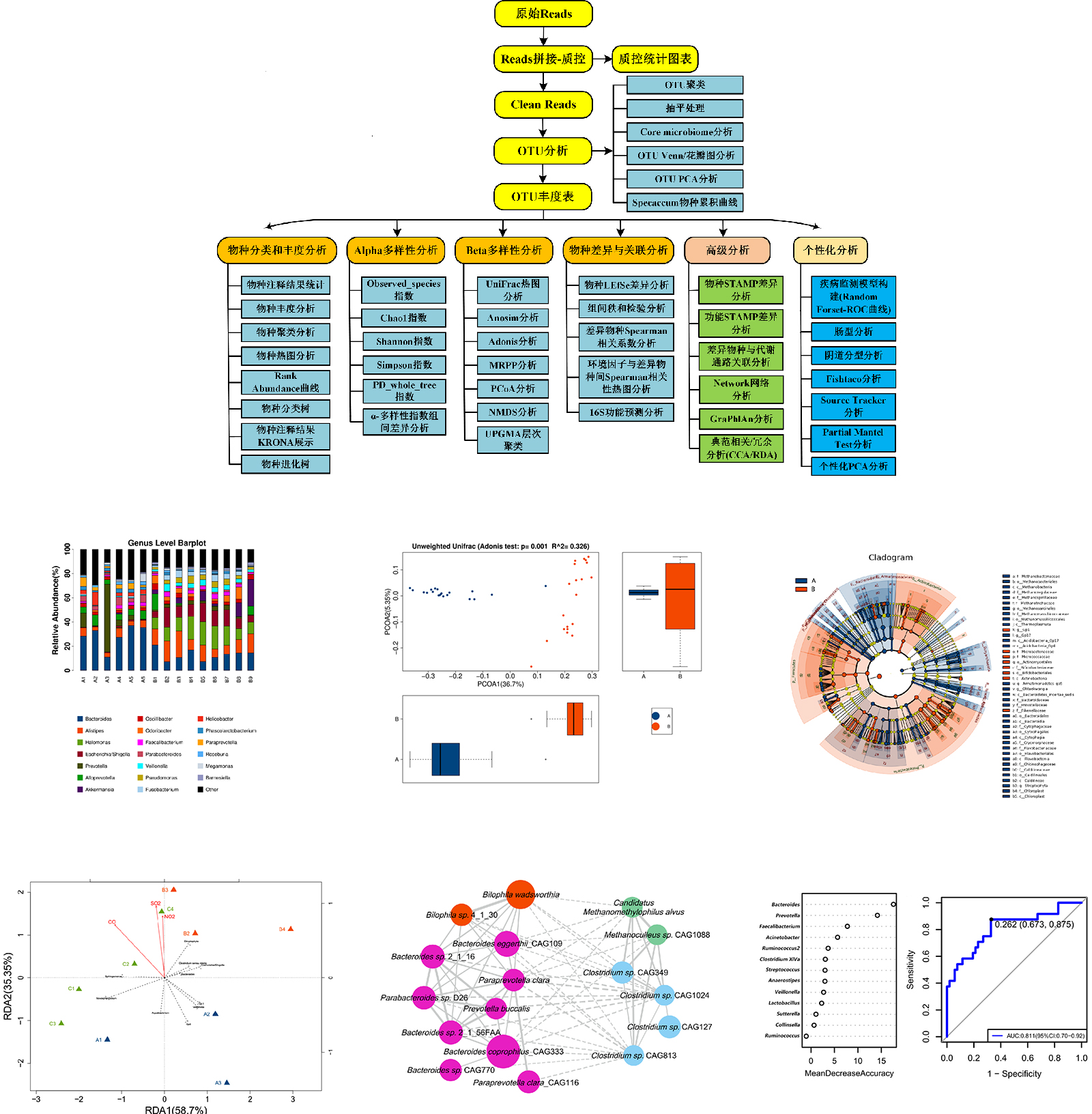
 Technical workflow
Technical workflow

 Bioinformatics analysis pipeline and partial results presentation
Bioinformatics analysis pipeline and partial results presentation
 Application areas
Application areas
1、Medical field: The relationship between diseases and the human microbiota, such as metabolic diseases, gastrointestinal disorders, autoimmune diseases, cancer, neurological diseases, and other illnesses.
2、Livestock field: The interaction between microbial communities in the gut, rumen, and other animal systems and factors like animal reproduction, growth and development, nutritional health, immunity, and disease treatment.
3、Agricultural field: The interaction between rhizosphere microorganisms and plants, agricultural practices/fertilizer treatments, and soil microbial communities.
4、Environmental field: The microbial composition of specific environments (polluted environments like smog and dust, residential and commercial environments), distribution and composition of microbial communities during organic fertilizer fermentation, wastewater treatment, petroleum degradation, water bodies, and marine environments.
5、Extreme environments: Study of microbial communities in extreme environmental conditions.





