Metagenomic sequencing
Metagenomic sequencing refers to the use of high-throughput sequencing technologies to study the genomes of microorganisms in a specific environment. It involves the application of bioinformatics analysis methods to investigate microbial diversity, community structure, explore potential microbial functions, and understand their interactions with the environment. Compared to traditional microbiome research methods, metagenomic sequencing overcomes the limitations of cultivating certain microorganisms, enabling rapid and efficient acquisition of genomic information from the entire microbial community. As a result, this technology has been widely applied in various studies of environmental microbiology in recent years.
 Platform and Strategy
Platform and Strategy
Platform and Strategy
Illumina sequencing platform,PE150
 Technical workflow
Technical workflow

 Bioinformatics analysis pipeline and partial results presentation
Bioinformatics analysis pipeline and partial results presentation
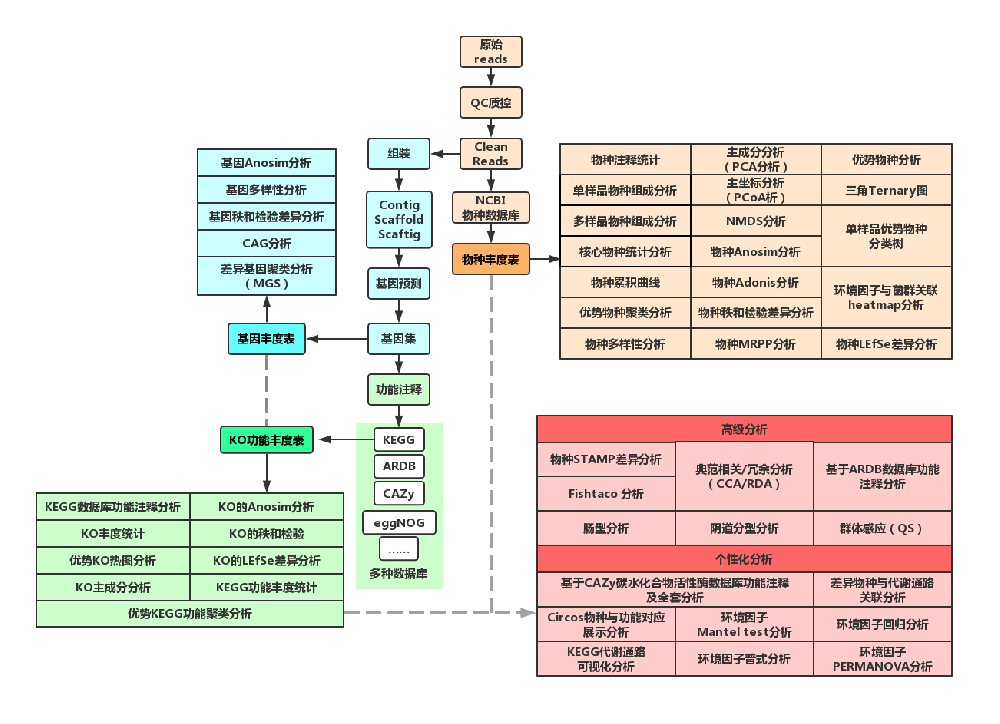 |
| 生物信息分析流程 |
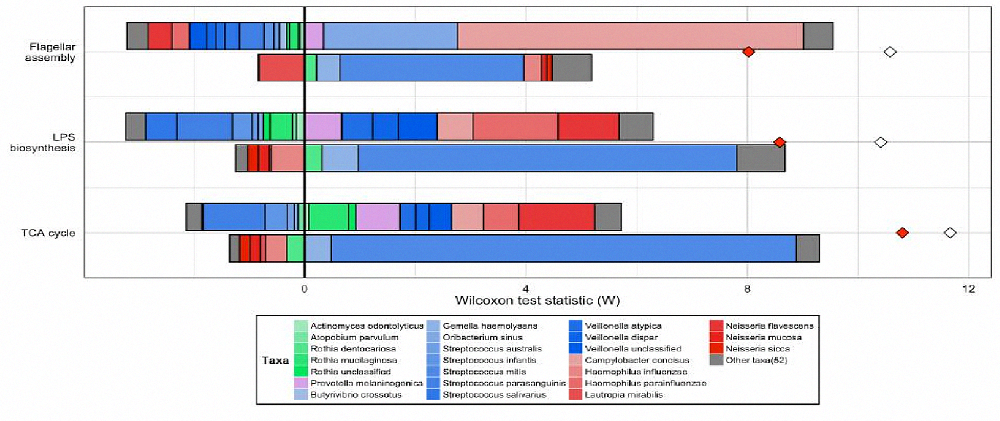 |
| 物种对代谢通路贡献度Fishtaco分析 |
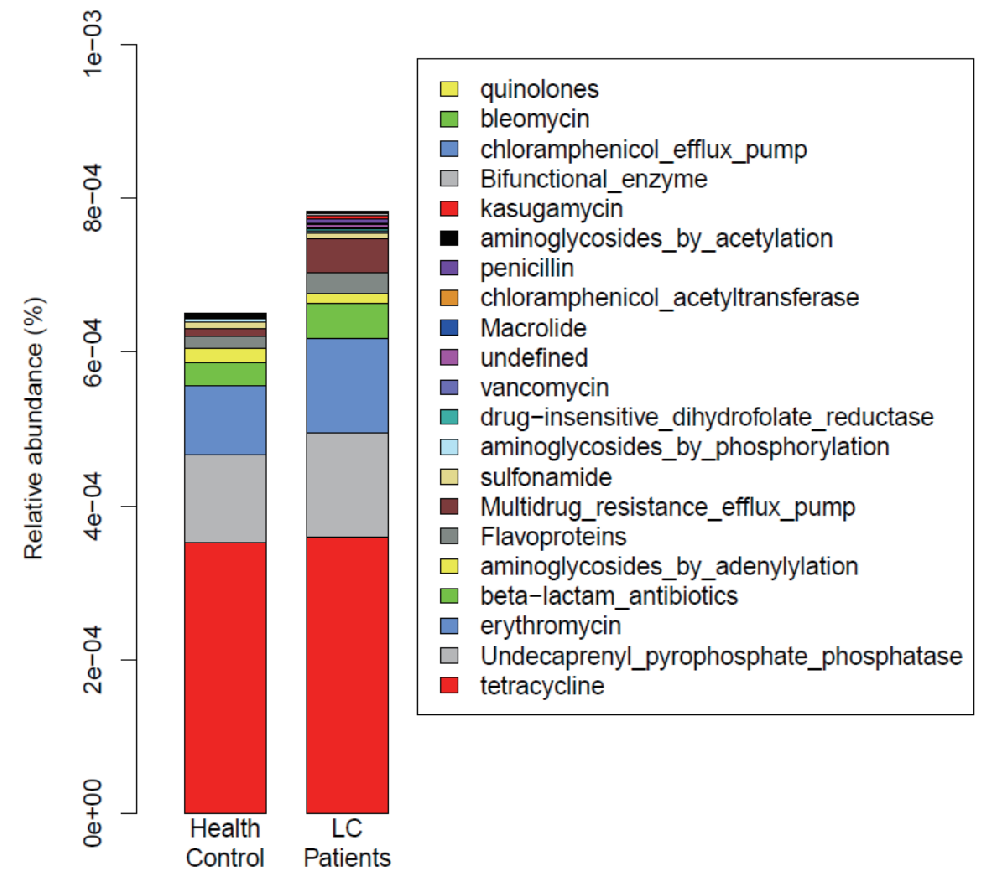 | 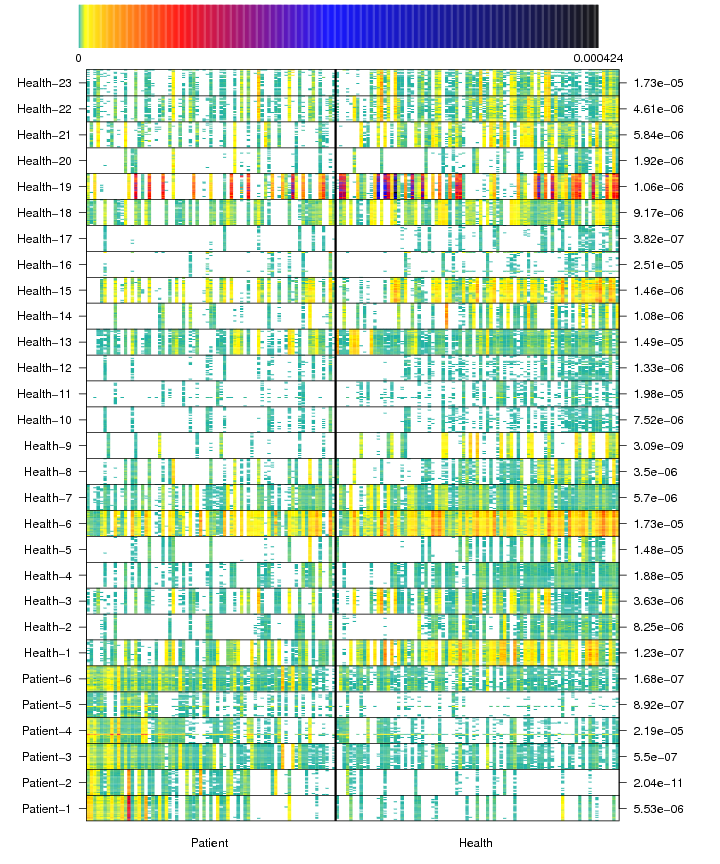 |
| 耐药基因各分类的分布图 | MGS丰度热图 |
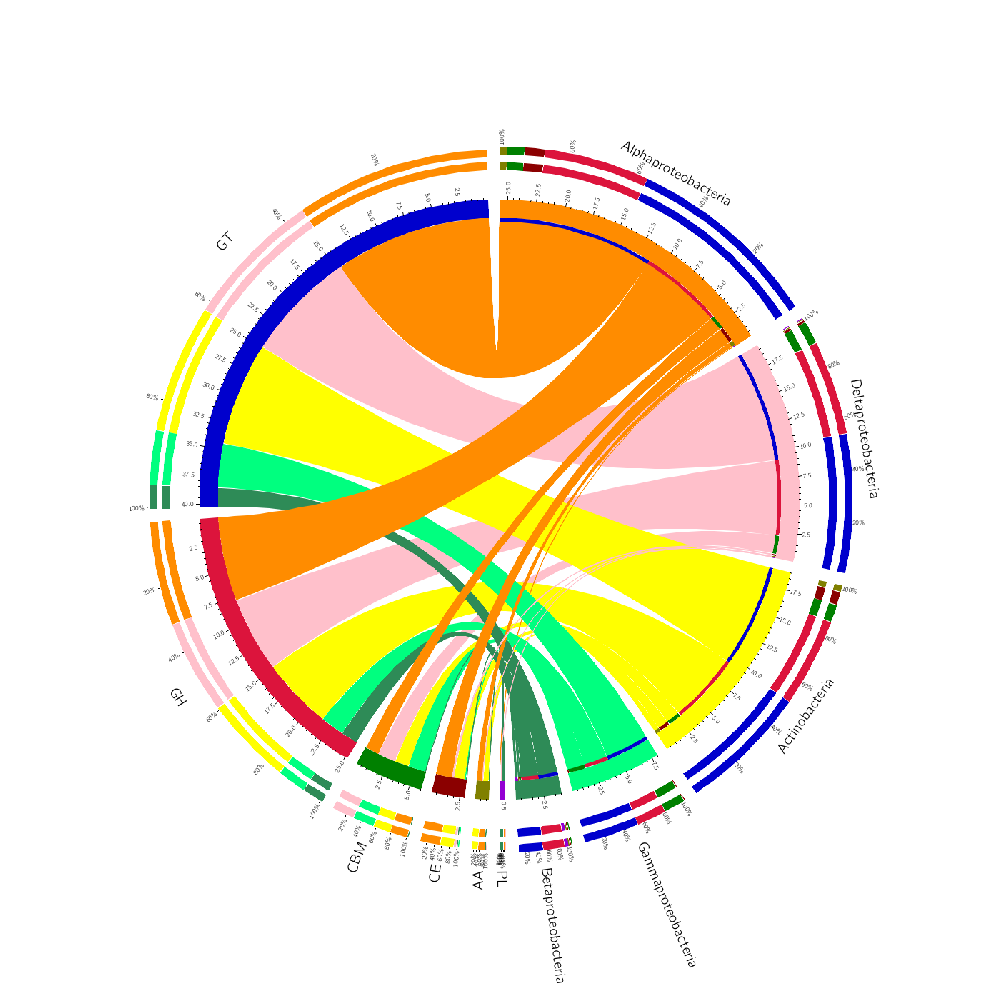 | 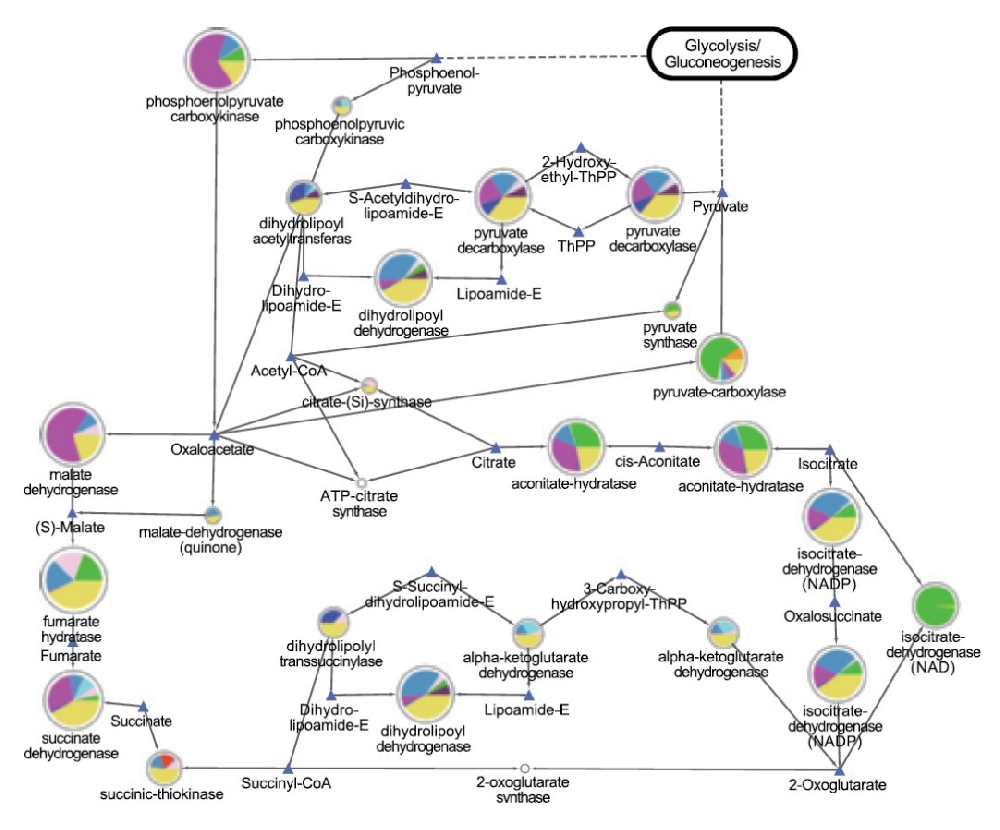 |
| CAZy基因家族与物种信息对应的Circos分析 | KEGG代谢通路可视化分析 |
 Application areas
Application areas
Metagenomic sequencing is suitable for studying the entire microbial community in a specific environment without the need for isolation and culturing. It involves directly extracting DNA from environmental samples for sequencing, and investigating the community structure, species classification, gene functions, and related metabolic pathways of environmental microorganisms.
Currently, it has been widely applied in the following fields:
1、Medical field: the relationship between diseases and human microbiota, such as metabolic diseases, digestive diseases, autoimmune diseases, tumors/cancers, neurological diseases, and other diseases;
2、Livestock field: the interaction between microbial communities in the gut, rumen, and animals' reproduction, growth, development, nutrition, health, immunity, and disease treatment;
3、Agriculture field: the interaction between root-associated microorganisms and plants, agricultural practices/fertilizer treatments, and soil microbial communities;
4、Environmental field: microbial community composition in specific environments (polluted environments such as haze, dust, residential and commercial environments), organic fertilizer fermentation treatment, sewage treatment, petroleum degradation, microbial community distribution, gene function, and metabolic networks in water and marine environments;
5、Extreme environments: research on microbial communities under extreme environmental conditions.





